Government Imposter Scams: A Growing Threat
In a recent survey conducted by Interac a staggering 42% of respondents said they had been targeted by a Government Impersonation Scam, making them one of the most common types of scams. Government Imposter Scams are nothing new but as technology and the internet continue to evolve so do the means by which scammers commit these frauds. Which is why it’s important to stay informed about the latest types of government imposter scams and how they are being perpetrated.
What are Government Imposter Scams?
Government Imposter or Government Impersonation scams are a type of scam that involve individuals or groups posing as representatives of government agencies to deceive victims into giving over personal information or money. There are many ways these scams play out but there are few more common scenarios that scammers tend towards.
Common Types of Government Impersonation Scams
IRS/CRA Scams
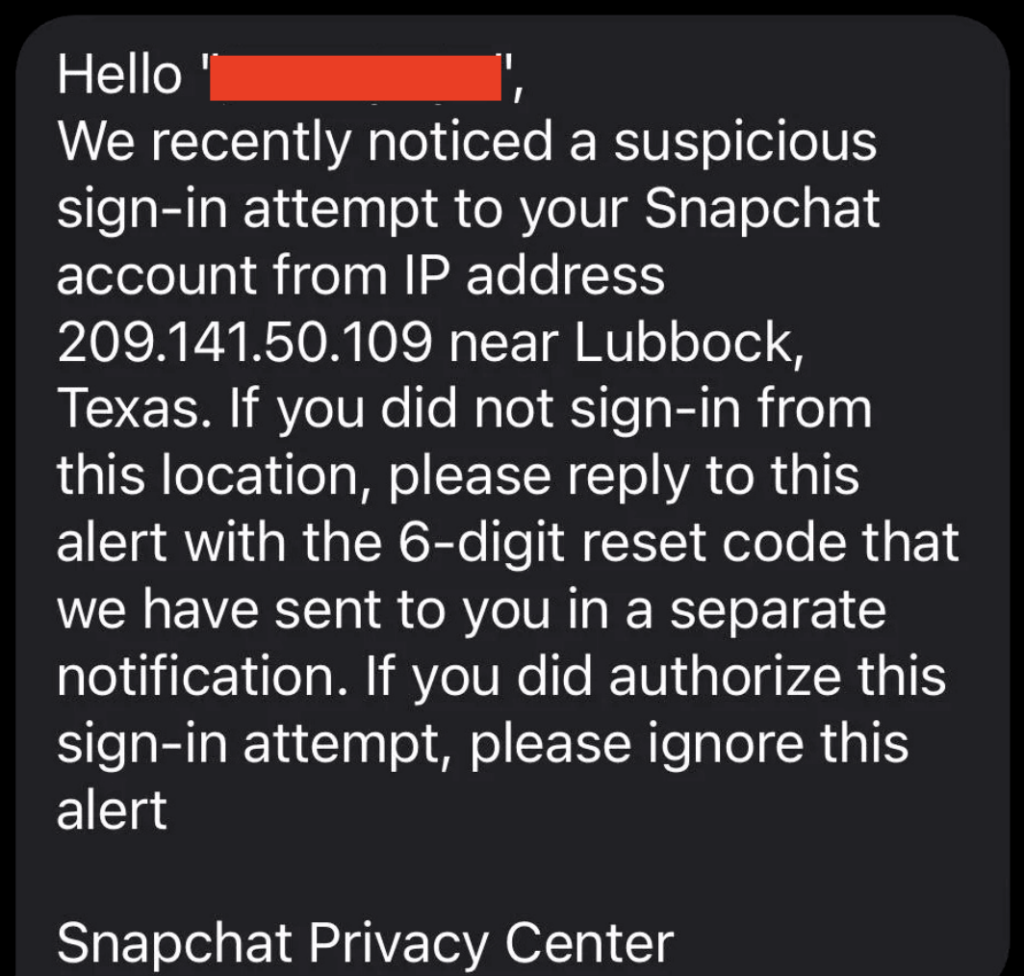
A scammer contacts a target claiming to be an employee of either the CRA/IRS. They may state that you have an outstanding case against you, owe back taxes, have unpaid balances or committed a financial crime. They then will threaten arrest, fines or even deportation if the money is not paid. They generally will request payment via transfer, pre‐paid cards, gift cards or crypto.
Social Security/Insurance Scams
Social Security scams aim to deceive people into providing sensitive personal information, such as Social Security numbers They may claim that there has been illegal activity under your SSN/SIN, or that there is some sort of bogus benefit or a cost of living adjustment you are eligible for but you need to provide for SSN to claim it
Medicare/Medicaid/Healthcare Scams
There are several common types of scams Medicare/healthcare related scams. They include:
- Pressure to Switch Plans: Fraudulent calls, often posing as Medicare, may offer “pre-approved” plans with lower costs, but insist on a fee for enrollment.
- Card Renewal Notices: Watch out for calls demanding activation, renewal, or upgrades for your Medicare card, requesting your Medicare number or payment for processing.
- Coverage Threats: Scammers might claim issues with your Medicare account, threatening to cancel benefits unless you immediately provide personal information or join a new plan.
- Refund Offers: Beware of scams suggesting eligibility for plan-related refunds. Scammers may ask for Medicare and bank details. Stay informed and vigilant to protect yourself from Medicare fraud.
Law Enforcement Scams
Law enforcement scams involve fraudulent attempts by individuals or groups to impersonate law enforcement officers or agencies. These scams often play on people’s trust in authority figures and use fear tactics to manipulate victims into providing money, personal information, or both. Two common types of law enforcement scams include the package scam, in which victims are told a package addressed to them, containing illegal goods, has been intercepted. As well as the Laundry card scam where the Victim is told that their bank card has been used in a money laundering scheme and their accounts are going to be locked.
How Scammers Contact You
Understanding how scammers reach out is crucial to recognizing potential threats. Whether it’s through phone calls, emails, or text messages, staying vigilant is key.
General Warning Signs:
Most communications from scammers show some common red flags.
- Unsolicited Contact: Beware of messages or calls that unexpectedly reach you, especially from unfamiliar sources.
- Requests for Sensitive Information via Insecure Channels: Exercise caution when asked to share personal or confidential details through unsecured platforms.
- Urgency and Threats: Be wary of communications creating a sense of urgency accompanied by threats or intimidating language.
- Encouragement to Click on Links or Open Attachments: Exercise discretion if prompted to click on links or open attachments, especially in unexpected or suspicious messages.
- Unconventional Payment Requests: Stay vigilant when faced with demands for money through unconventional methods or untraceable transactions.
How to Handle Scam Texts, Calls, and Emails
Knowing how to respond when faced with a potential scam is vital. Here are some general guidelines:
| Texts | Delete or mark as spam, then block the number. |
| Calls | Don’t engage; hang up and block the number. |
| Emails | Mark as spam and block the sender. |
Verify Before You Trust
Always verify the legitimacy of communications from government departments. Contact the official communication channel or log into secure online accounts to confirm the authenticity of messages.
Be Proactive: Protect Your Personal Information
The best way to protect yourself against government imposter scams it is important to take proactive steps.
- Invest in a reliable protection system.
- Use VPNs and visit only secure sites.
- Utilize a password manager and create strong passwords.
- Be mindful of oversharing online.
- Regularly review and update privacy settings.
I’ve Been Scammed… Now What?
If you have been the victim of a government impersonation scam (or any type of scam) it is important to take several steps to prevent further damage or loss. You can follow Aura’s comprehensive Victim Checklist (full details here).
- Don’t blame yourself
- Stop paying scammers
- Check your insurance coverage
- Act quickly to assess the full damage
- Notify your bank, lenders
- Set up a fraud alert or credit freeze
- Secure your online accounts
- Gather documents and proof for your fraud case
- Report fraud and identity theft to the FTC
- File a police report
- Try to recover lost funds
- Dispute fraudulent transactions
Where to Report Scams

FTC (Federal Trade Commission)
Online: reportfraud.ftc.gov
Call: 1-877-FTC-HELP (382-4357)

Anti Fraud Centre
Online: antifraudcentre-centreantifraude.ca
Call: 1-888-495-8501